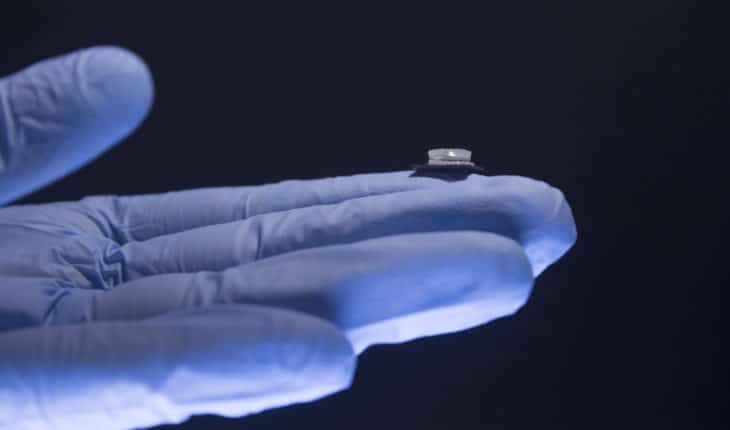
A tiny new silicon-based lab-on-chip test could pave the way for cheap handheld infectious disease testing.
The chip, developed at Imperial College London and known as TriSilix, is a ‘micro laboratory’ which performs a miniature version of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the spot. PCR is the gold-standard test for detecting viruses and bacteria in biological samples such as bodily fluids, faeces, or environmental samples.
Although PCR is usually performed in a laboratory, which means test results aren’t immediately available, this new lab-on-a-chip can process and present results in a matter of minutes.
The chip is made from silicon, the same material that is used to make electronic chips. Silicon itself is cheap, however, it is expensive to process into chips which requires massive, ‘extremely clean’ factories otherwise known as cleanrooms. To make the new lab-on-chip, the researchers developed a series of methods to produce the chips in a standard laboratory, cutting the costs and time they take to fabricate, potentially allowing them to be produced anywhere in the world.
Lead researcher Dr Firat Guder of Imperial’s Department of Bioengineering said: “Rather than sending swabs to the lab or going to a clinic, the lab could come to you on a fingernail-sized chip. You would use the test much like how people with diabetes use blood sugar tests, by providing a sample and waiting for results – except this time it’s for infectious diseases.”
The paper was published in Nature Communications.
The researchers have so far used TriSilix to diagnose a bacterial infection mainly present in animals as well as a synthetic version of the genetic material from SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19.
The researchers say the system could in future be mounted onto handheld blood sugar test-style devices. This would let people test themselves and receive results at home for colds, flu, recurrent infections like those of the urinary tract (UTIs), and COVID-19.
Table-top devices for testing of infections like COVID-19 already exist, but these tests can be time-consuming and costly since the patient must go to a clinic, have a sample taken by a healthcare worker and go home or stay in clinic to wait. People leaving their homes when not feeling well increases the risk of spread of a pathogen to others.
If validated on human samples, this new test could provide results outside a clinic, at home or on-the-go within minutes.
The researchers also say a highly portable test could accelerate diagnosis of infections and reduce costs by eliminating transportation of samples. Such tests could be performed by citizens in the absence of highly trained medical professionals – hence, if they need to self-isolate, they can start immediately without potentially infecting others.
Making testing more accessible and cheaper is especially important for people in rural areas of low-income countries, where clinics can be far away and expensive to travel to. If made available to patients, it could also be used to diagnose and monitor infections like UTIs, which often recur despite antibiotics.
First author Dr Estefania Nunez-Bajo, also of the Department of Bioengineering, said: “Monitoring infections at home could even help patients, with the help of their doctor, to personalise and tailor their antibiotic use to help reduce the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.”
Each lab-on-a-chip contains a DNA sensor, temperature detector and heater to automate the testing process. A typical smartphone battery could power up to 35 tests on a single charge.
Next, the researchers plan to validate their chip with clinical samples, automate the preparation of samples and advance their handheld electronics. They are looking for partners and funders to help accelerate the translation of the technology to deliver testing at resource limited settings at homes, farms or remote locations in the developing world.
- Combination of drugs could prevent thousands of heart attacks - 21st April 2025
- UQ Study Links Poor Teen Diets to Heavy Social Media Use - 21st April 2025
- Gut microbiome could delay onset of type 1 diabetes - 3rd April 2025